In FAM, there are a variety of elements that can be used on your Family form. Each element functions differently.
Before you build an online form, consider the data you wish to collect, the fields that will pre-populate your form and the fields to which you will upload collected data. Determine which element type will best suit each step of your form, and plan the order of elements.
Form elements will be highlighted in pink if they are not valid for the particular form Type you have selected.
Element Attributes
Elements can have:
- Labels – This is the text displayed to the left of an element.
- Values – These are the options presented to the right of a given element on a form; and
- Attributes – These define the formatting of the element as it displays on the form. When you create an element, attributes may appear as default settings in the Edit Element window.
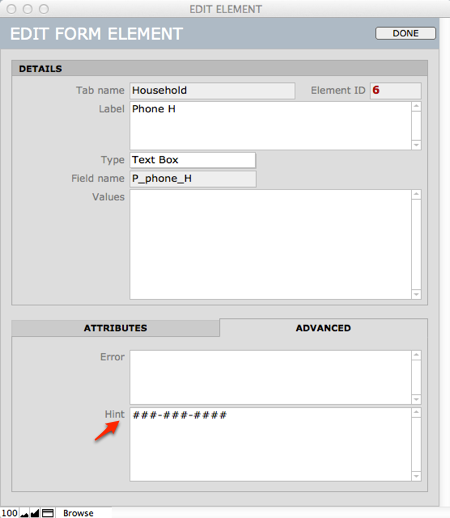
- Hints – These display an example of how an answer might be formatted (as for the desired format of a phone number).
Editing Elements
Edit any element on your form by clicking the green arrow at the right end of the element row:
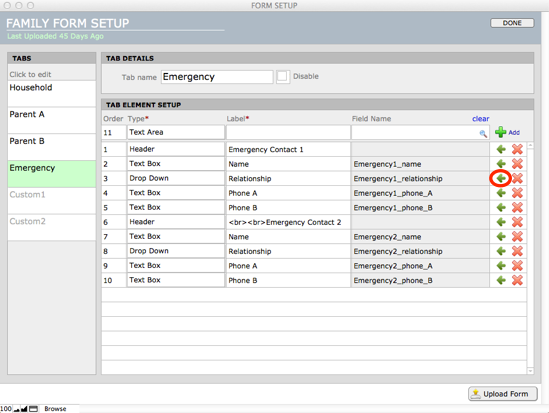
This leads to the Edit Element window, where you can enter:
- Values and Attributes (Attribute tab)
- Hints (Advanced tab)
NOTE: Use the character called a Substitution pipe (typed as shift+backslash) to separate the value that will pass into your solution (on the left) from the value that will display on your form.

Elements whose contents are editable by the family on the web
TEXT BOX
A Text Box is an editable, single line, text entry box. It may display data from your solution. You are expecting the family to enter new data or review/edit the pre-populated data from the core solution.
![]()
TEXT AREA
A Text Area is a multi-line text entry box. Families can enter longer responses here. There is no practical character limit. A Text Area can be pre-populated with editable data (e.g. medical data from the previous year).
Use Attributes to specify the size of the frame (a certain number of characters wide, or a certain number of lines tall), such as:
- characterWidth|40 – This text area will be 40 characters wide.
- visibleLines|10 – This text area will be 10 lines tall, with a scroll bar active if there are more lines.

DATE DROP DOWN
A Date Drop Down is a cluster of three drop-down menus, for Month, Day, Year.
Use Value to specify the text for ghost labeling in the three fields (MM, DD, YYYY) (that is, the label appears inside the field container).
The Attributes determine:
- the order of the date fields (MM/DD/YYYY or DD/MM/YYY)
- whether the fields are separated by slashes or hyphens
- which years display as choices
by entering the following:
- format|MM/DD/YYYY – Use slashes to separate your date fields.
- format|MM-DD-YYYY – Use hyphens to separate your date fields.
- yearRange|30 – Thirty years will display in the YYYY drop down.
- yearStart|1990 – The thirty year list will begin with the year 1990.
DATE PANEL
A Date Panel is a cluster of three fields (MM / DD / YYYY) in which Month, Day, Year is manually entered.
![]()
Use Values to specify the text for ghost labeling in the three fields (MM, DD, YYYY) (that is, the label appears inside the field container).
Use Attributes to specify the order of fields, the separator (“/” or “-“), and the list of years (Drop Down only), such as:
- format|MM/DD/YYYY – Use slashes to separate your date fields.
- format|MM-DD-YYYY – Use hyphens to separate your date fields.
Elements offering the family a choice
CHECKBOX
A single Checkbox offers the opportunity to respond Yes (I want this).
If you seek a single YES value, this box collects the boolean value of “1” if selected or “null” if not selected. This checkbox will check the corresponding checkbox in your core solution.
- Use the Label (which appears to the left of the checkbox) to enter your text;
- Enter “1” as the Field Value.
CHECKBOX GROUP
A Checkbox Group gives you one or more checkboxes grouped together under one header. Multiple boxes can be selected.
If you display a multiple choice list in which multiple boxes may be selected, the data that will be returned to the mapped field in your solution will be the data that appear to the right of the checkbox on the form. If you want to display long descriptive values on the form, but pass shorter text into your solution, use the Substitution pipe as you define Values.
To display a list of values, each Value must be separated by a carriage return.
Use Attributes to specify the number of columns or rows:
- columns|1 – Checkboxes or radio buttons will appear vertically, in one column
- rows|5 – Checkboxes or radio buttons will appear horizontally, in one row (keep labels short)
RADIO GROUP
A Radio Group offers multiple choices, with only one answer possible. It offers one or more radio buttons grouped together under one label. Only a single value is returned. The data that will be imported into your solution is the value that appears to the right of the selected radio button. A radio group allows you to use descriptive text for a list of 2-6 options.
Values and Attributes of a Radio Group are identical to a Checkbox Group (above).
DROP DOWN
A Drop Down element displays a drop-down list of values where you expect the end-user to choose one value from a long list. A Drop Down element is an alternative to a Radio Group, since it returns only a single value.
NOTE: When creating a Value list for a Drop Down menu, always begin your list with a blank line at the top. If you do not have a blank line at the top of the list—and one of your values appears at the top—you can never be certain that the end user chose the value. It is possible that they skipped the question and the top value is returned by default.
MULTISELECT LIST
In a Multiselect List, your list of choices will appear in a box with each item on a separate line. Use Attribute to set the number of lines that will display by default. If there are more choices/Values than the number of lines, your box will have a scroll bar. Multiple lines can be selected by clicking Command+ the next item.
In Values, use a Substitution pipe to separate value|display.
Use Attributes to specify size of the frame, such as:
- characterWidth|40 – This text area will be 40 characters wide.
- visibleLines|10 – This text area will be 10 lines tall, with a scroll bar active if there are more lines.
Elements that are display only (not editable)
HEADER
A Header is designed to introduce a new section of your form. It is un-editable text that by default is aligned at the far left of the form.
Use Attributes to specify horizontal alignment (left, center, right), such as:
- horizontalAlignment|center – This header will be centered in the form.
- horizontalAlignment|left – This header will be aligned left.
PARAGRAPH
A Paragraph element displays an un-editable block of text that spans the width of the page.
Use Attributes to specify horizontal alignment (left, center, right), such as:
- horizontalAlignment|center – This header will be centered in the form.
- horizontalAlignment|left – This header will be aligned left.
READ ONLY
A Read Only field has a label on the left and displays content from your solution in the field area on the right. If you are sending up a calculated field from your solution, or another field that you do not want the end user to change, this is probably how you want to display it.

